Create a Logical Data Model Manually
Once you have generated the physical data model (PDM) either using the API or in the LDM Modeler, create the logical data model (LDM) manually in the LDM Modeler.
If you cannot or do not want to create the LDM manually, you can generate the LDM automatically using the API or in the LDM Modeler.
Creating the LDM manually is suitable for the following situations:
- Your database contains the complex analytical scenarios.
- Your database stores only a part of the metadata (for example, relations are handled by application logic and not by foreign keys in the database).
- You want to first create the LDM and then define your analytic use cases based on it.
- You want to build your analytic experience iteratively, customize, and evolve your LDM. In this case, consider the following:
- If you make custom changes to the LDM and then automatically generate the LDM later, the custom changes will be overwritten.
- If you regularly update the relational model of your database, maintaining the LDM manually can be very costly and even not possible in some cases.
To create the LDM manually, do the following:
- Create datasets.
- Map the LDM to the PDM.
- Set the primary key in datasets.
- Create relationships between the datasets.
- Add Date datasets.
- Publish the LDM.
Create Datasets
Steps:
Open your workspace.
Click the Data tab.
The LDM Modeler opens in view mode.
Click Edit.
The LDM Modeler is switched to edit mode. You can see the registered data sources in the left panel.
If you do not have any data source, you cannot generate the LDM. Create a data source first.To add a dataset, drag Empty dataset from the left panel and drop it in the blank canvas area.
Select the newly added dataset, click More… -> View details.
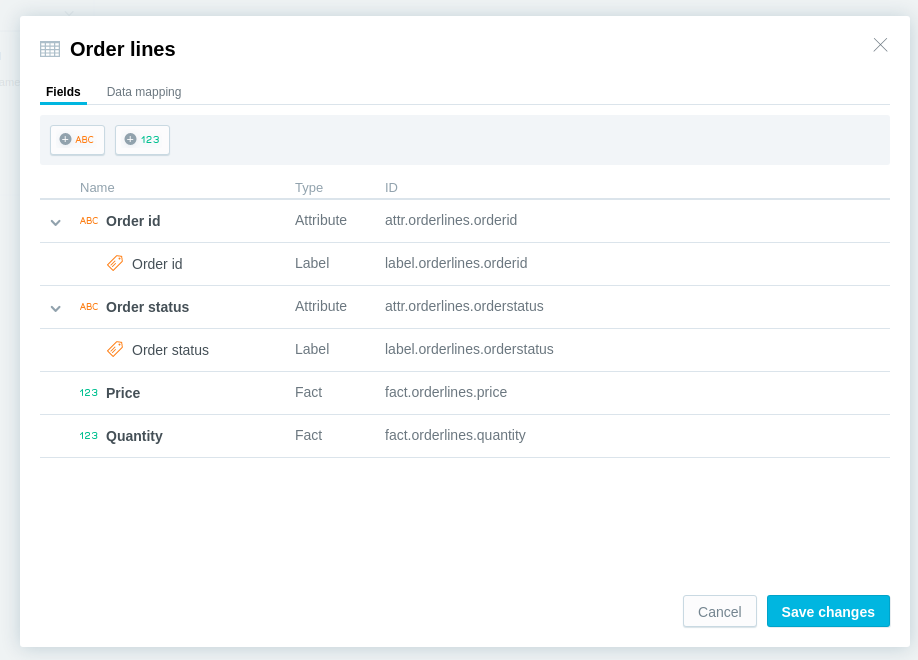
Add fields (facts, attributes, and attribute labels) to the dataset.
Create as many datasets as you need.
Here is the example of a manually created dataset named Order lines:
Map the LDM to the PDM
Mapping your LDM to the PDM allows you to use the data from your database when you create insights.
The LDM focuses on your analytic needs and may not match the relational model of your database. Before mapping the LDM to the PDM, you may need to alter the relational model and introduce data transformation operations.
Steps:
Click Scan next to the data source that represents your database.
The scan dialog opens.
De-select the Generate datasets checkbox to prevent automatic generation of datasets.
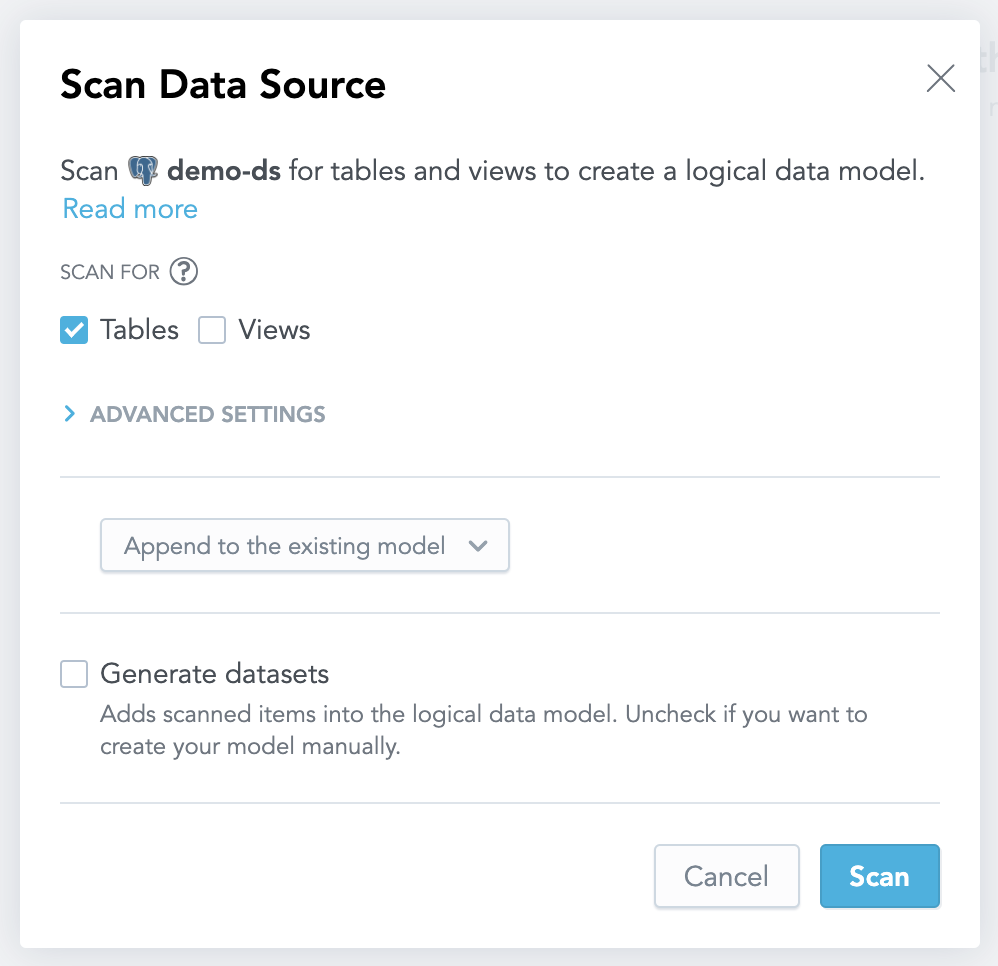
Click Scan.
The scanning process starts. It scans the physical tables/views in your database so that you can then map the LDM components to the tables/views and columns in your database through the PDM (that is, map the datasets to the tables/views and map the attributes/facts/references to the table/view columns).
When the scanning completes, you see a confirmation message.
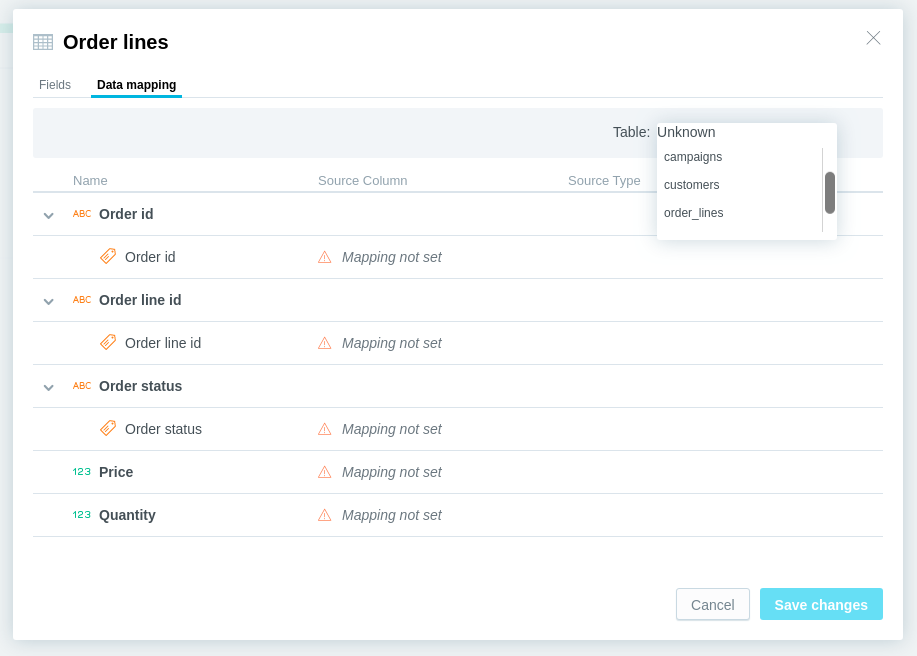
Set up mapping for all the datasets in your LDM.
Select a dataset, click More… -> View details.
Click the Data mapping tab.
Map the dataset to a particular table in your database.
Map each field in the dataset to a specific column in this table.
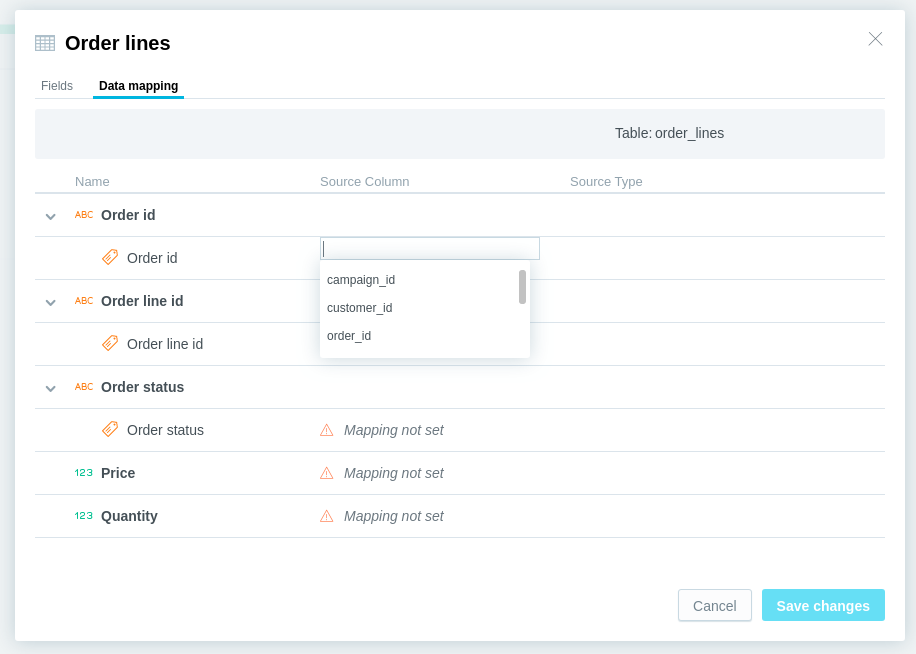
Click Save changes.
Repeat Steps 1-5 for every dataset.
Set the Primary Key in Datasets
Set the primary key (grain) for each dataset in your LDM.
The LDM Modeler supports only simple primary keys. Compound primary keys are not supported. Create an artificial simple primary key in your database.
Steps:
Select a dataset, and click More… -> Set primary key.
Select the attribute that should become the primary key, and click Set key.
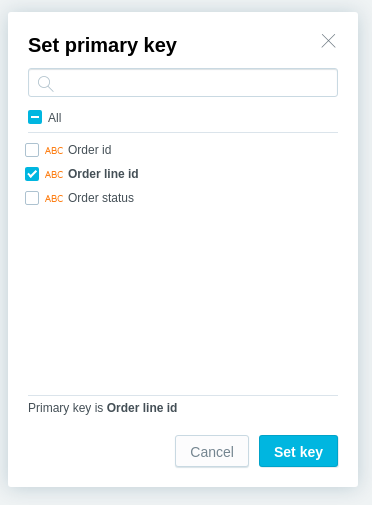
The dialog closes, and the primary key is set.
Repeat Steps 1-2 for every dataset in your LDM.
Create Relationships between the Datasets
A relationship between two datasets allows you to use information from one dataset to slice the data in the other dataset. Creating relationships allows you to discover new analytical scenarios when creating insights.
Creating a relationship requires a primary key in one of those datasets.
Steps:
Locate the datasets that you want to create a relationship between.
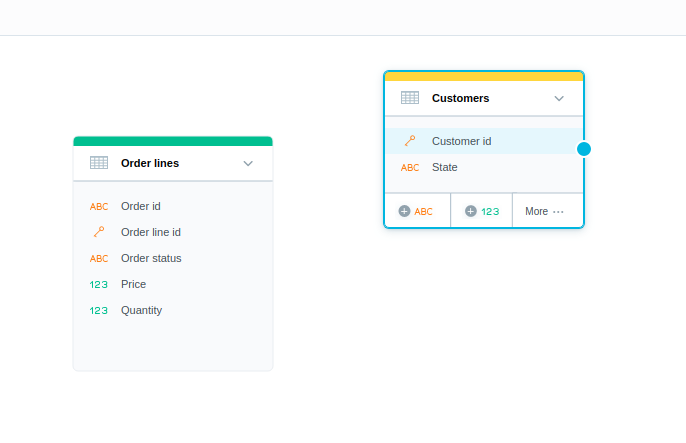
Select the dataset from which you want to start a relationship. Click the blue dot on the right border of the dataset and drag the arrow that appears to connect it to the other dataset.
The relationship is created.
In the following image, the
Customersdataset is connected to theOrder linesdataset.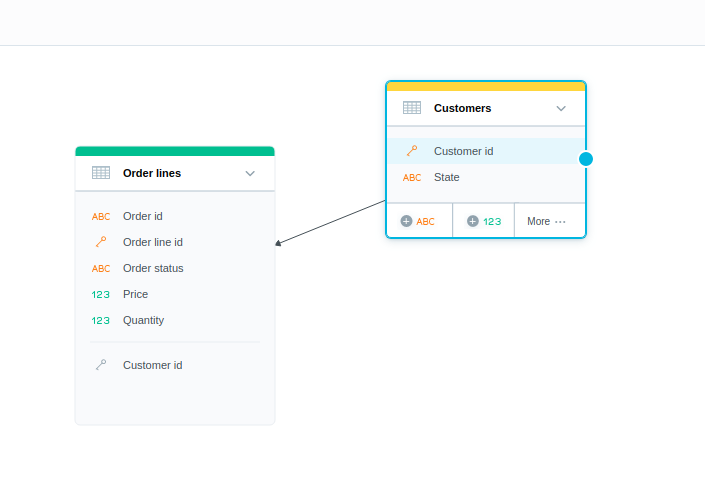
Notice that the
Order linesdataset has been extended by theCustomer idforeign key.Select the dataset where the foreign key was added to, click More… -> View details, then click the Data mapping tab.
Locate the newly added foreign key, and map it to a column in the table that is mapped to the dataset (the foreign key column).

Repeat Steps 1-4 for all the datasets in your LDM that you want to connect.
Add Date Datasets
A Date dataset is a dataset that represents DATE / TIMESTAMP columns in your database. The Date dataset helps you manage time-based data and enables aggregation at the day, week, month, quarter, and year level.
Steps:
Drag Date from the left panel and drop it in the blank canvas area.

Create a relationship between the new Date dataset and a dataset that contains a date/timestamp column.
In the following image, the dataset with a date/timestamp column is the
Order linesdataset.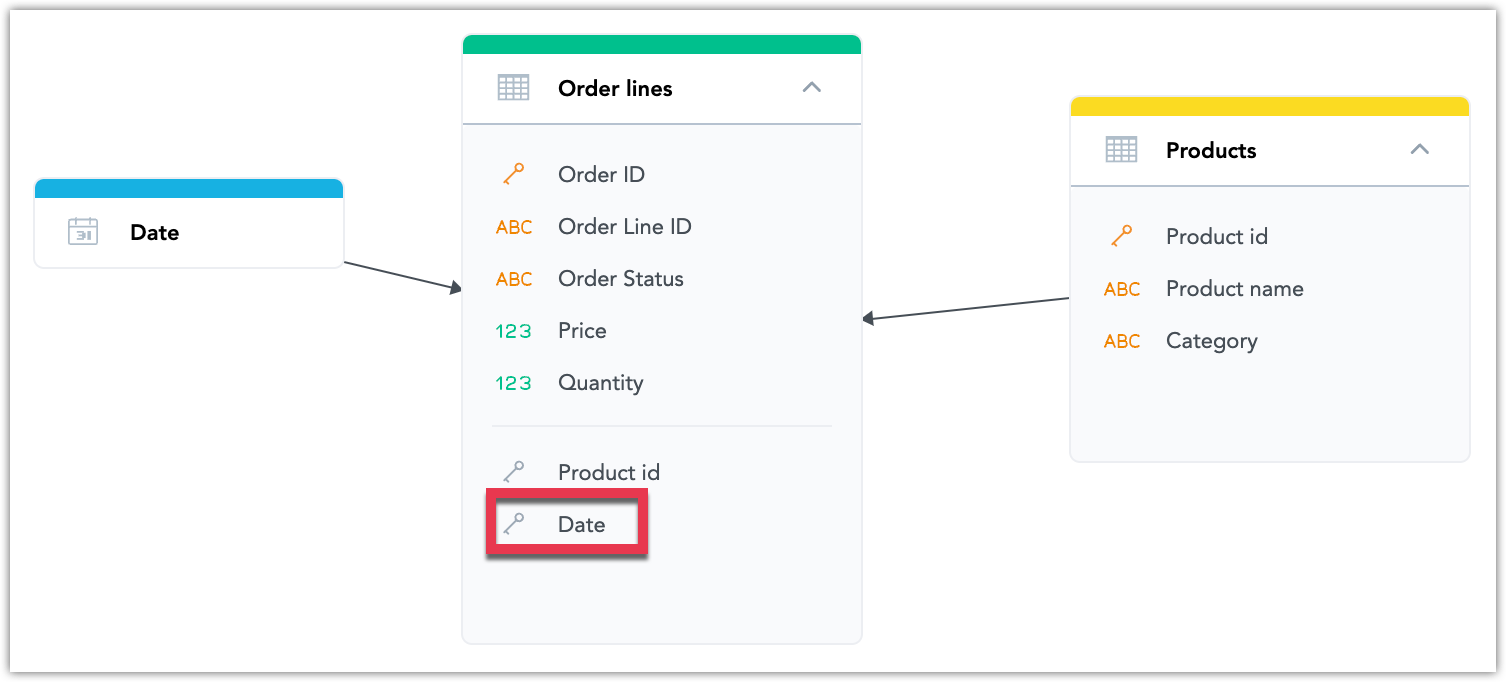
Notice that the
Order linesdataset has been extended by theDateforeign key.Select the dataset where the foreign key was added to, click More… -> View details, then click the Data mapping tab.
Locate the newly added
Dateforeign key, and map it to a column in the table that is mapped to the dataset (the foreign key column).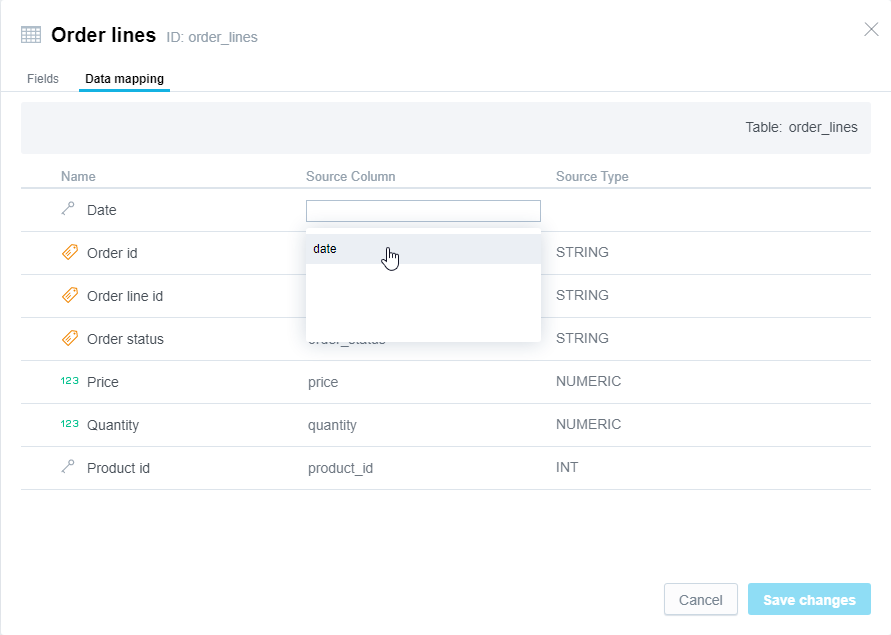
(Optional) Configure the Date dataset.
Select the dataset, and click Details.
In the configuration dialog, configure the dataset as needed:
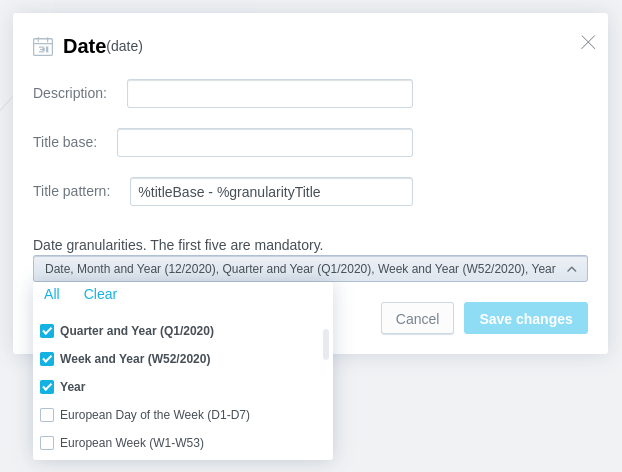
Add a description to the dataset.
Configure how the name of the included date/time granularity levels will be displayed.
The
Title patternfield defines the general format for the titles of all included granularity levels. Use the%titleBaseand%granularityTitleplaceholders to define the order in which the value from theTitle basefield and the default granularity title will be used in the title. IfTitle baseis not specified, the default name of the Date dataset (Date) will be used (for example,Date - Year,Date - Hour, and so on).Select the date/time granularity levels that you want to include in the Date dataset.
Some date granularity levels are selected by default and cannot be excluded from the Date dataset.
Create as many Date datasets as you need.
Publish the LDM
To publish the LDM, follow the instructions from this article.
Once you have the LDM published, you can start building insights and dashboards.