COUNT
Use COUNT to return the number of unique values for an attribute.
- For large amounts of data where complete accuracy is not a priority, consider using APPROXIMATE_COUNT to increase the processing speed. APPROXIMATE_COUNT is available only for workspaces that use Vertica as a data source.
Syntax
COUNT uses the following syntax:
| Form | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|
| single parameter | SELECT COUNT(attribute) | SELECT COUNT({attribute/order_id}) |
| two parameters | SELECT COUNT(attribute, primary_key) | SELECT COUNT({attribute/order_id}, {attribute/campaign_id}) |
| with USING | SELECT COUNT(attribute) USING primary_key | SELECT COUNT({attribute/order_id}) USING {attribute/campaign_id} |
Single-Parameter Version
The single-parameter version of COUNT dynamically gets the context of where to count from the insight it is used in.
Two-Parameter Version
In the two-parameter version, the context where to count the attribute is determined explicitly by the second parameter - the primary key of the dataset.
The primary key is connection point between datasets. It connects the COUNT function’s first parameter to the dataset in which the count is to take place.
Specifying COUNT Context Resolution with USING
You deploy the USING keyword in logical data models with ambiguous connection points.
The context for computation of COUNT may be ambiguous if there are
multiple fact tables which relate to a counted attribute. Imagine a
model with fact datasets Purchase_Fact and Sales_Fact that are both
connected to the Store and Product attributes.
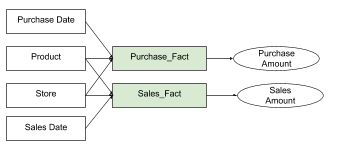
If you build an insight that displays the count of products per
store with SELECT COUNT({attribute/product}) and slice it with Store, it would not
compute because it is ambiguous if the insight displays the
number of unique products that have been purchased by store or the
number of unique products that have been sold by the store.
In a metric, USING provides a hint for which context should be used. For
example the insight will show the number of unique purchased products per
store if Purchase_Fact attribute is placed into the USING clause
SELECT COUNT({attribute/product}) USING {attribute/purchase_fact}.
The attribute in the USING clause does not need to be from the actual
fact table, it can also be another attribute which uniquely determines
the correct context (e.g. use of the Purchase Date attribute in the
USING clause directs the use of the Purchase_Fact dataset to join
Product with Store because Sales_Fact does not directly relate to
Purchase Date).