Set Up Data Filters for Users
Overview
User data filters (also user data permissions or row-level security) allow you to restrict data that are available for specific users in specific workspaces.
By setting a data filter, you can define what subset of the data in a workspace will be available for individual users or user groups.
As opposed to workspace data filters (that point to a specific column in a specific table), user data filters use MAQL expressions. This offers you more flexibility in creating complex conditions because the filters are applied to any connected data rather than a specific database columns.
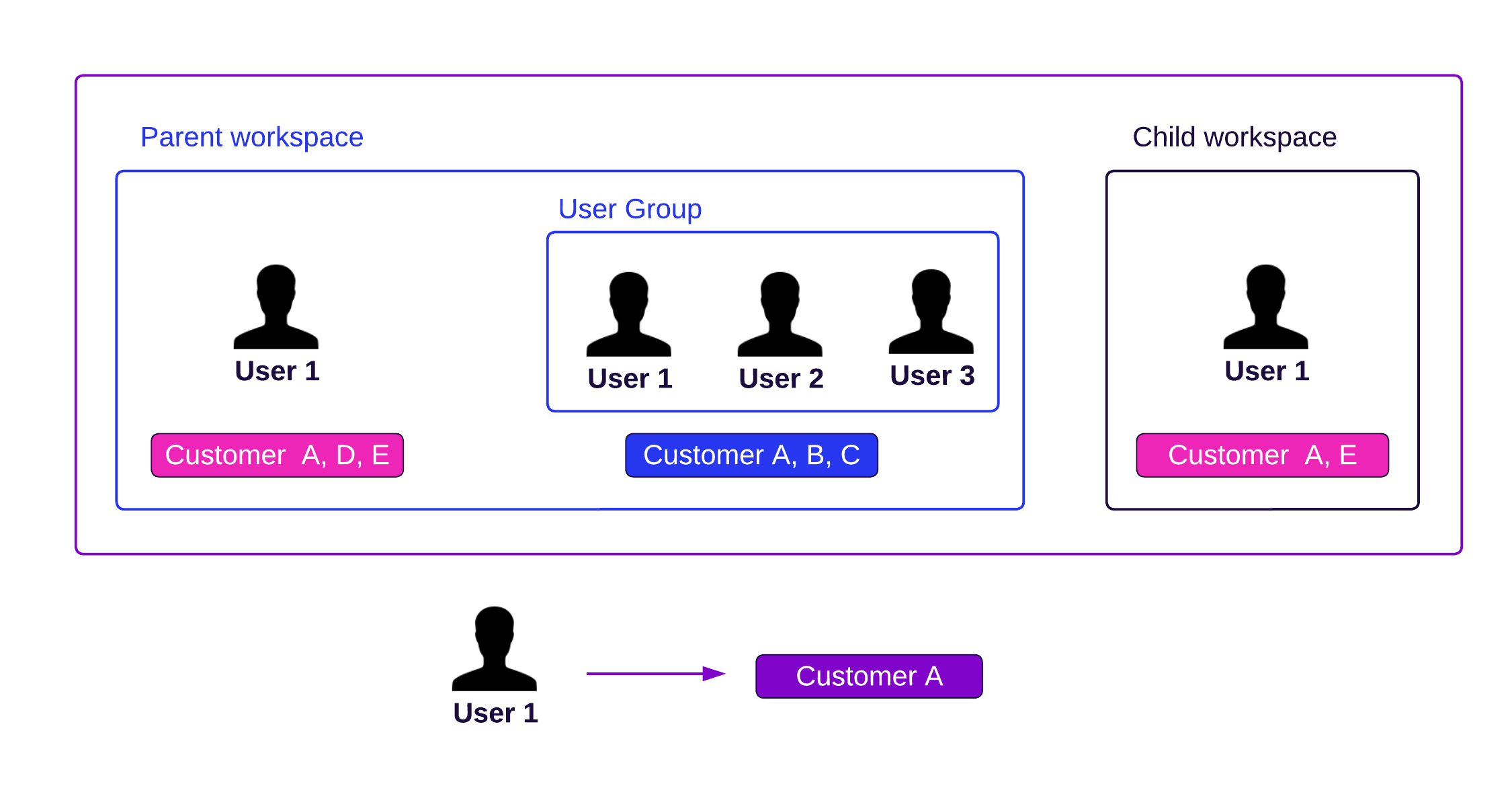
Multiple User Data Filters
You can restrict data for individual users and user groups, or combine them.
The effective filters for individual users are inherited from all user groups that the user is a member of throughout the workspace hierarchy.
For example, if a user is a member of any user groups and filters are created for these groups as well, then also all filters from these groups are applied (using the AND operator).
Set Up User Data Filters
You can set up user data filteres via:
Entity API
This enables you to create, replace, update, and delete individual user data filters.
Declarative API
This enables you to update a complete set of user data filters.
To set up user data filters, do the following:
To create user data filters, you must have MANAGE permissions for the organization or workspace. For details about permissions, see Manage Permissions.
Create JSON Document
Use the following template to create a JSON document that describes the user data filters that you want to apply:
{
"data": {
"type": "userDataFilter",
"id": "<data-filter-id>",
"attributes": {
"maql": "<maql-expression>",
"title": "<data-filter-name>"
},
"relationships": {
"user": {
"data": {
"id": "<user-id>",
"type": "user"
}
}
}
}
}
<data-filter-id>is the unique ID of the user data filter.<maql-expression>is the definition of the filters using MAQL.<data-filter-name>is the UI-friendly name of the user data filter.<user-id>is the ID of the user that the user data filter with the specified condition is applied to.
Example: A sample JSON document.
{
"data": {
"type": "userDataFilter",
"id": "filter1",
"attributes": {
"maql": "{label/l_linestatus} = \"O\"",
"title": "Status filter"
},
"relationships": {
"user": {
"data": {
"id": "user1",
"type": "user"
}
}
}
}
}
Use the following template to create a JSON document that describes the user data filters that you want to apply:
{
"userDataFilters": [
{
"id": "<data-filter-id>",
"maql": "<maql-expression>",
"title": "<data-filter-name>",
"user": {
"id": "<user-id>",
"type": "user"
}
}
]
}
<data-filter-id>is the unique ID of the user data filter.<maql-expression>is the definition of the filters using MAQL.<data-filter-name>is the UI-friendly name of the user data filter.<user-id>is the ID of the user that the user data filter with the specified condition is applied to.
Example: A sample JSON document.
{
"userDataFilters": [
{
"id": "filter1",
"maql": "{label/l_linestatus} = \"O\"",
"title": "Status filter",
"user": {
"id": "user1",
"type": "user"
}
}
]
}
You can use userGroup instead of user to apply the filter to all users from a user group.
Add JSON Document to Workspace
To add the user data filters to the workspace, run the following:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/workspaces/<workspace-id>/userDataFilters \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \
-d @/path/to/your-filter-definition.json
To list all filters that are created in the workspace, run the following:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/workspaces/<workspace-id>/userDataFilters/ \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN"
To update the user data filters, run the following:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/layout/workspaces/<workspace-id>/userDataFilters \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X PUT \
-d @/path/to/your-filter-definition.json